Sign Convention
The program uses three right-handed coordinate systems:
1. Global Coordinate System
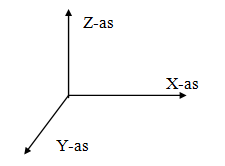
The position of this global coordinate system is arbitrary. The XY-plane coincides with the plane of the frame. This coordinate system is used for defining node coordinates, node restrictions, and node loads. Calculated node displacements and support reactions are displayed relative to this coordinate system.
2. Member Coordinate System
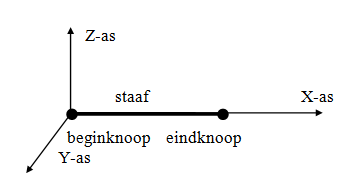
The origin of this coordinate system is always at the start node of the member in question. The XY-plane coincides with the plane of the frame. The X-axis coincides with the member axis.
3. Node Coordinate System
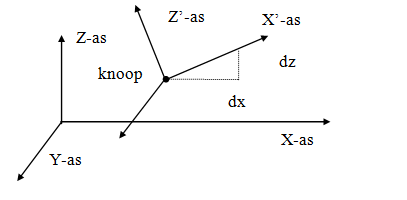
A local (node) coordinate system can be specified. The origin lies at the node in question. The direction of the X-axis is determined by specifying a relative dx and dz from the node. (see the figure above). Local coordinate systems can be used to specify node restrictions (supports or 'restrains'), node loads, and/or node displacements in any direction.
Sign Rules
Input and output data are displayed relative to the coordinate systems described above.
- A force in the direction of the positive X- or Z-axis is considered positive.
- A moment rotating from the positive X-axis to the positive Z-axis (according to the corkscrew rule) is positive.
- A moment opposite to the clockwise direction is positive.